Initial Management of Bone Fractures
Fractures are breaks in bones that occur due to trauma, falls, or underlying medical conditions. Prompt and proper initial management is essential to reduce pain, prevent complications, and promote proper healing. The first response to a fracture can significantly impact the patient’s recovery.
1. Assessment and Safety
- Ensure safety: Before approaching the patient, make sure the environment is safe.
- Check vital signs: Assess airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs) to rule out life-threatening injuries.
- Evaluate the injury: Look for deformity, swelling, bruising, and open wounds. Note the affected limb’s position and any abnormal movement.
2. Pain Control
- Administer pain relief if available, such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs.
- Avoid moving the fractured limb unnecessarily to prevent further pain or damage.
"Fractures are not just breaks in bone, but breaks in function. Early stabilization saves lives and limbs." Dr. John Hunter, Father of Modern Surgery
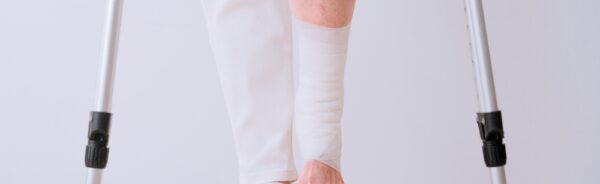
3. Immobilization
- Immobilization is critical to prevent further injury to bones, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Use splints, braces, or slings to stabilize the fracture.
- Ensure the immobilization covers joints above and below the fracture site.
- For suspected spinal fractures, use a cervical collar and keep the patient on a firm surface until professional help arrives.
4. Control Bleeding and Open Wounds
- If the fracture is open (bone protruding through the skin), cover it with a sterile dressing.
- Apply gentle pressure around the wound to control bleeding, but avoid pressing directly on exposed bone.
- Do not attempt to push bones back into place.
5. Reduce Swelling
- Elevate the injured limb above heart level if possible.
- Apply ice packs wrapped in cloth for 15–20 minutes at a time. Avoid direct contact with skin to prevent frostbite.
6. Avoid Complications
- Monitor for signs of shock: pale skin, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, or fainting.
- Watch for neurovascular compromise: numbness, tingling, or loss of pulse in the affected limb.
7. Seek Medical Care
- All fractures require evaluation by a healthcare professional.
- X-rays or other imaging are needed to determine the type and severity of the fracture.
- Follow-up may include casting, surgical intervention, or physiotherapy depending on the injury.
Conclusion
Immediate and careful management of bone fractures can prevent complications, reduce pain, and improve healing outcomes. Stabilization, pain control, and timely medical care are the pillars of first aid for fractures. Remember, do not attempt to realign bones unless trained to do so.
March 6, 2024
Foods That Support and Strengthen Bone Health
March 6, 2024
Spine Health: The Foundation of a Pain-Free Life